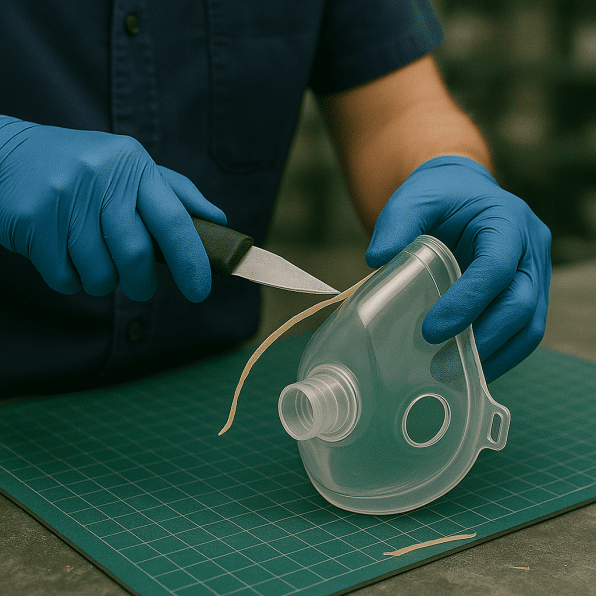
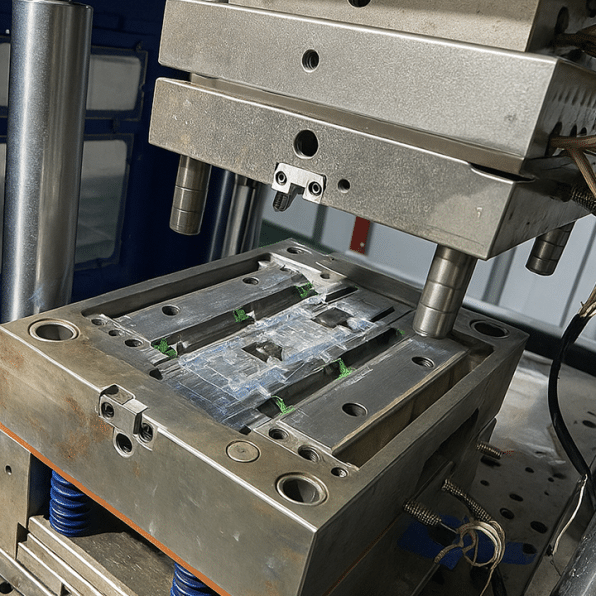
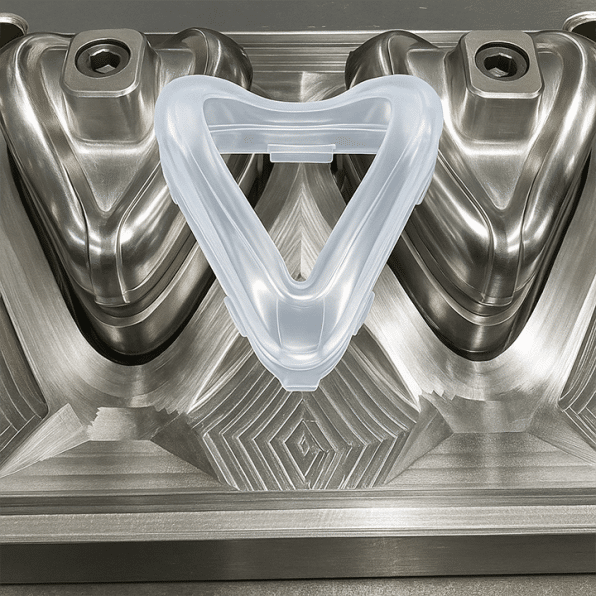
How Does Silicone Molding Work?
Advantages & Disadvantages of Silicone Molding
Advantages
-
Low Tooling Costs
LSR molds are simple to design and manufacture compared to injection molds. This makes silicone molding attractive for prototypes and small-to-medium production runs, where speed and cost-efficiency are often big priorities.
-
Material Versatility
A wide variety of silicone compounds are available, including formulations that serve specific purposes – such as creating parts that are flame retardant or meet medical grade specifications. Ultimately, the process serves the performance needs of a diverse range of industries.
-
Part Quality
LSR parts tend to have strong mechanical properties, outstanding heat resistance and good chemical stability. They are durable and maintain their performance in demanding environments.
-
Tight Dimensions
Silicone molding can produce parts with consistent dimensions and smooth surface finishes.
-
Well-Suited to Larger Parts
Silicone compression molding produces parts with thicker walls or larger sizes more effectively than some other molding processes. This includes injection molding with silicone.
Disadvantages
-
Longer Cycle Times
The mixing and curing processes required by liquid silicone molding result in a longer per-part production time than injection molding.
-
Labor Requirements
For best results, mold flow analyses should be performed to validate mold, gating and venting designs. Pilot production runs are also highly recommended to optimize the molding process. Once optimized, it’s a very consistent and reliable molding process.