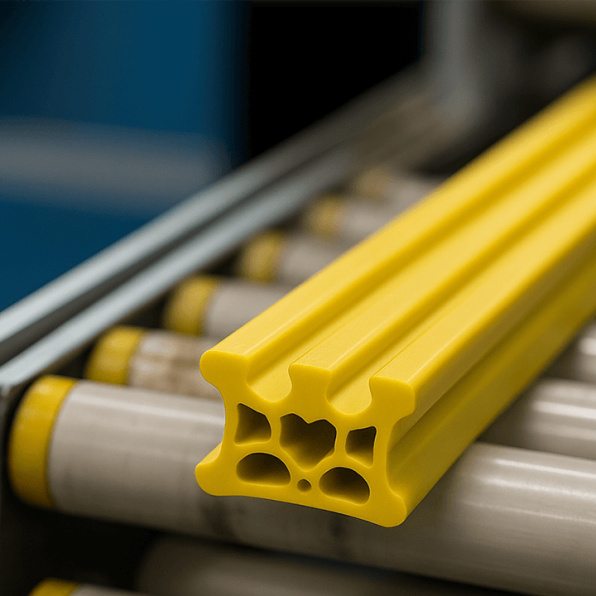
How Does Plastic Extrusion Work?
Is Plastic Extrusion A Fit For Your Needs?
Advantages
-
Cost-Effective
The continuous plastic extrusion process combines high production efficiency with minimal material waste. It is a cost-effective choice for large-scale manufacturing runs.
-
Consistent Quality
Plastic extrusion lends itself to consistency – especially uniform material flow and proper sizing. This results in smooth surface finishes and high quality across long production runs.
-
Flexibility
Custom-designed dies enable the production of complex cross-sections. This helps manufacturers meet specific design and application requirements.
-
Versatile Materials
A wide variety of thermoplastics can be used – with each offering different properties such as strength, flexibility or UV resistance. Products therefore can be tailored to a variety of applications, both indoor and outdoor.
Disadvantages
-
Initial Costs
Creating custom dies and tooling involves significant upfront investment. This makes plastic extrusion impractical for prototyping or short production runs.
-
Limited Shapes
Extrusion is best suited for parts with uniform cross-sections. Complex or irregular shapes with varying profiles are better suited to molding or machining methods.
-
Shrinking and Swelling
Plastic materials can expand when leaving the die – and contract during cooling. Achieving extremely tight tolerances can be challenging.