How Does High-Pressure Die Casting Work?
Is High-Pressure Die Casting a Fit For Your Needs?
Advantages
-
Precision
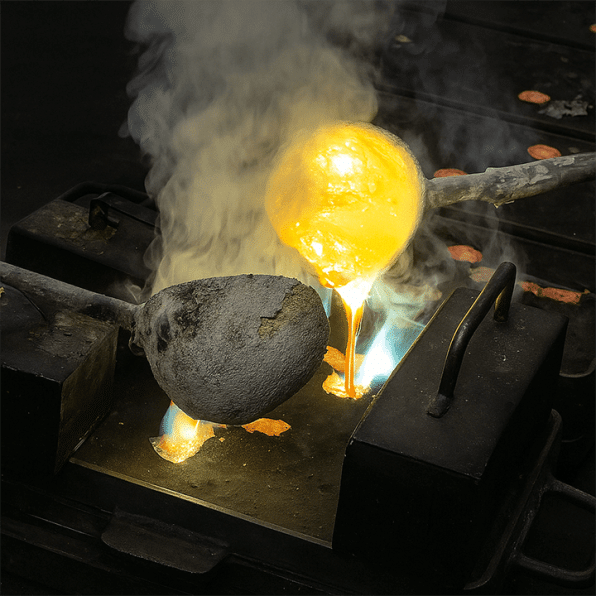
High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) can produce parts with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces that often do not require further machining. It is ideal for components such as automotive housings, where precision and aesthetic quality are critical.
-
Production Efficiency
This process is highly automated and has short cycle times, typically less than a minute per part. This enables large-volume production runs where quality is consistent and per-unit costs are low.
-
Complex Shapes and Thin Walls
The high pressure ensures filling of intricate features and thin walls. This enables the production of lightweight, compact designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other casting methods.
-
Mechanical Properties
Rapid solidification refines the metal’s microstructure, which improves strength and hardness. As a result, HPDC parts are often suitable for load-bearing or structural applications.
-
Minimal Post-Processing
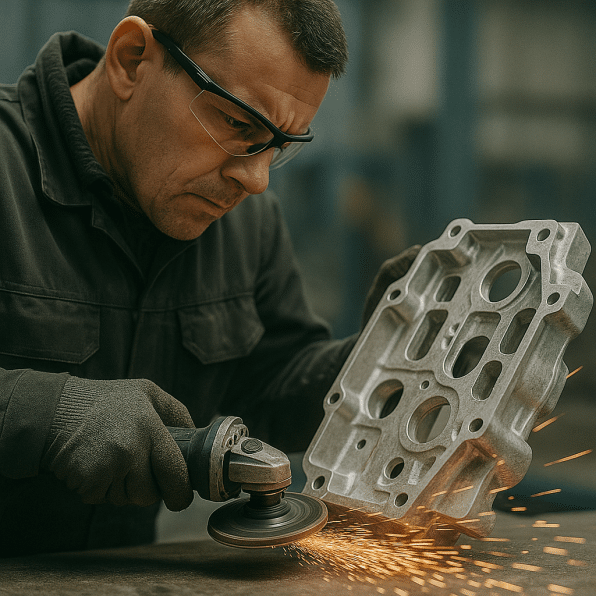
Parts often emerge with a near-net shape and smooth surface, requiring only trimming or light machining. This reduces finishing time and total manufacturing cost.
Disadvantages
-
High Initial Costs
Hardened steel dies are costly to create. Therefore, HPDC is mainly viable for high production runs, where tooling costs can be amortized over a large volume of parts.
-
Material Limitations
The high pressures involved in HPDC, and the fact the dies are made of steel, means the process is generally restricted to non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium and zinc. Ferrous metals would damage the die at required casting temperatures.
-
Porosity and Reduced Ductility
Internal porosity can occur if air is trapped during the injection process. This limits the use of HPDC parts in applications that require heat treatment or pressure-tight sealing.