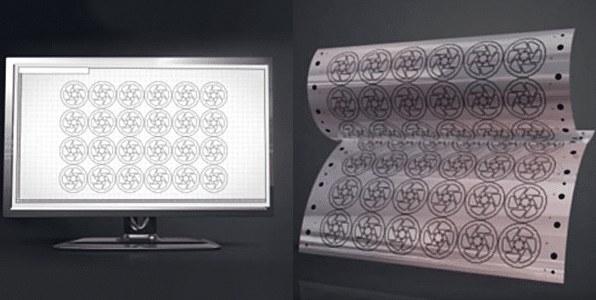
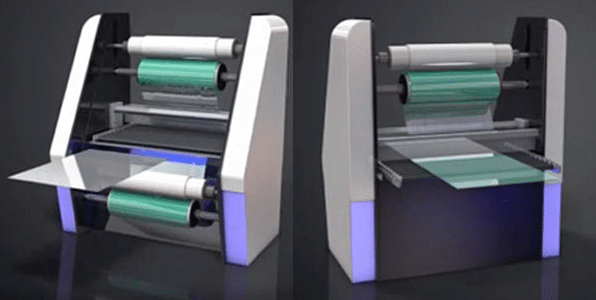
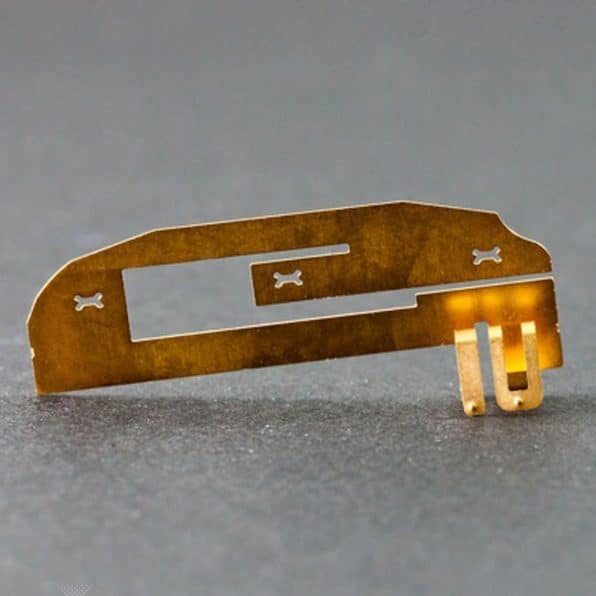
How Photochemical Machining Works
Is Photochemical Machining Right For Your Project?
Advantages
-
Fast Delivery
Because no hard tooling is required, we can fulfill many orders within a few days. Complex part designs may take up to a week. Photo chemical etching produces multiple parts from a single sheet of metal. Little or no finishing is required.
-
No Changes to the Integrity of the Metal
Many types of manufacturing, such as machining and laser cutting, can cause thermal stresses in the metal adjacent to the cut. They can also cause changes to the hardness, ductility or grain structure of the metal. Chemical milling doesn’t affect the internal structure of the metal.
-
Build Complex Yet Affordable Flat Parts
Industrial chemical machining enables you to create parts with fine details and complex geometries that aren’t possible to make using hard tools. You can also use it to fabricate parts in dead soft or full hard material without burrs or metal distortion.
-
Low-Cost Tooling
We produce films for photochemical machined parts directly from your CAD drawings. No hard tools or work-holding fixtures are needed. That helps to maximize the cost-effectiveness of photo chemical etching.
-
Easy, Fast & Inexpensive Prototype Parts
Photochemical machining uses films to create parts. That means you can iterate your designs quickly and affordably. The same process we use to create prototype parts is used to make your production parts.
-
Burr-Free Parts
Burrs are a common side effect of many types of metal processing. In contrast, the etching process produces a clean, smooth surface. It’s free of burrs and eliminates the need for manual finishing processes.
Disadvantages
-
Only For Thin Metal Parts
Photochemical machining is limited to relatively thin metals (1.5 mm or less)
-
Some Dimensional Inaccuracies
The etchant can sometimes undercut the edges of holes, leading to dimensional inaccuracies.
-
Only For Fabricating Flat Parts
Photochemical machining is a 2D process. It cannot be used to produce 3D parts.
-
Process Variables Must be Strictly Controlled
Inconsistent results can occur if process variables fluctuate, including etchant concentration, temperature or agitation.