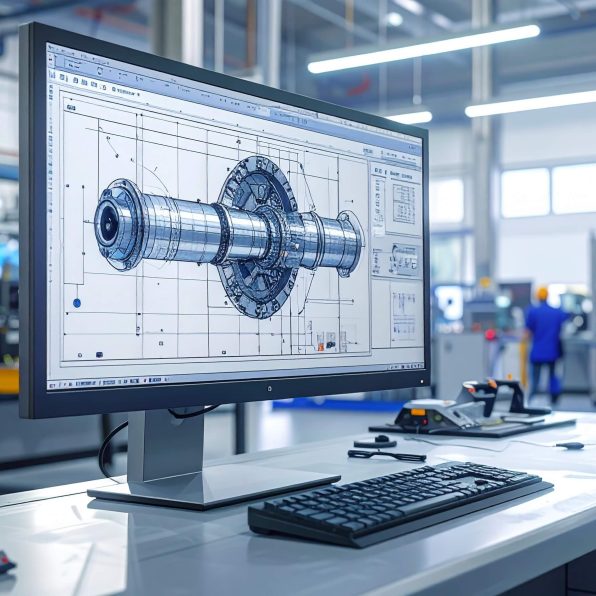
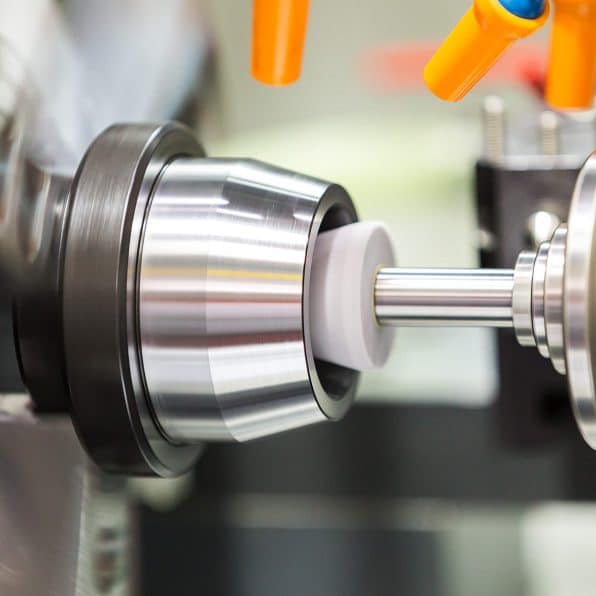
How CNC Turning Works
Is CNC Turning Right For Your Project?
Advantages
-
Precision & Accuracy
CNC turning can achieve extremely tight tolerances and produce parts with very high dimensional accuracy.
-
Consistency & Repeatability
The automated nature of the process ensures that every part produced is identical, which is crucial for mass production and consistent quality.
-
Reduced Waste & Lower Costs
The exceptional accuracy of CNC turning translates into reduced rework and waste, which helps to reduce per-part costs.
-
Versatility
CNC lathes can work with a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, allowing for a wide range of applications.
-
Excellent Surface Finish
CNC turning can produce parts with high-quality surface finishes, which is important for many industrial applications.
Disadvantages
-
Only Cylindrical Patrs
CNC turning is restricted to creating cylindrical and rotational-symmetry components, limiting its use for more complex shapes.Also, certain features and geometries cannot be machined using this method. Examples include curved holes, extremely thin walls and straight internal edges,
-
Production Limitations
While precise for single units, the process of producing one unit at a time can make it slow for large batches compared to other methods.
-
Skilled Operators Required
Skilled operators and programmers are required to setup, maintain and troubleshoot CNC turning machines. Mistakes in CAD/CAM programming can cause costly errors or downtime.