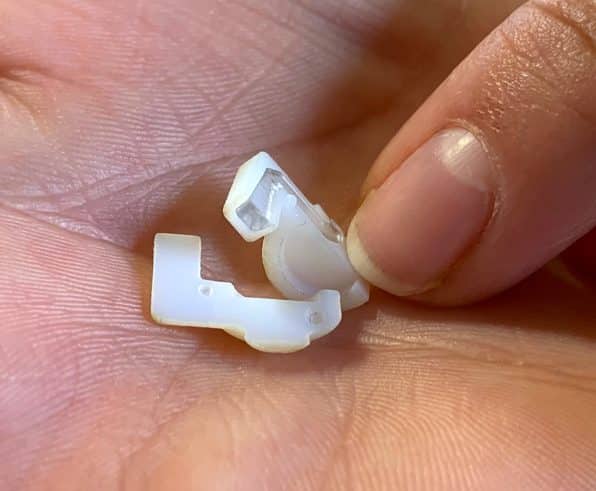
How Does PolyJet 3D Printing Work?
What Are the Advantages & Limitations of PolyJet 3D Printing?
Advantages
-
Versatile & Fast
From prototypes and colorful models to end-use parts, Fathom’s PolyJet printing service does it all. It can print them quickly, giving you more time to design, test and perfect your designs.
-
Excellent Level of Detail
PolyJet can print layers as thin as 16 microns. That means parts produced using it can contain an extraordinary amount of detail and an excellent surface finish.
-
Support for Digital Materials
PolyJet printers can mix up to six resins, which gives designers, engineers and your industrial 3D printing service unprecedented creative opportunities to fine-tune their part designs and material characteristics.
-
Transparent Options
PolyJet can print transparent materials that enable the production of transparent and translucent parts.
-
Fast Removal of Support Material
The gel-like support material used by PolyJet is water soluble. It can be dissolved using a water jet. This eliminates the need for time-consuming post-production processes and results in a smoother part finish than some other 3D printing processes.
-
Strong Parts
PolyJet can produce sturdy parts that have good tensile strength.
Disadvantages
-
Cost
The materials required for PolyJet printers tend to be more expensive than those for many other types of 3D printing.
-
Part Size Limitations
PolyJet isn’t suitable for printing larger parts.
-
Support Structure
Even though PolyJet uses a gel-like support structure, adding it contributes to longer total part printing times.
-
Not for Long-term Use
Exposure to heat, sunlight and humidity can cause photopolymers to lose some strength and durability.