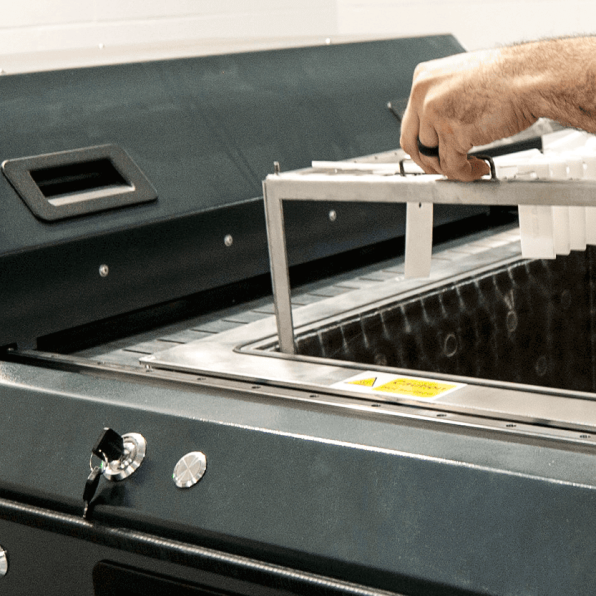
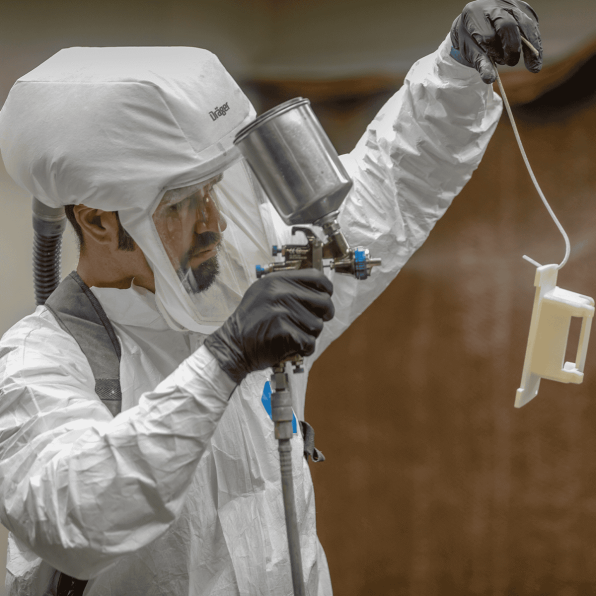
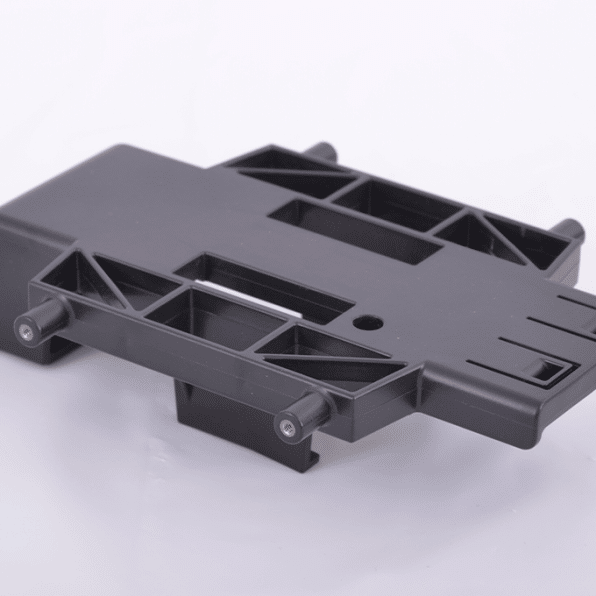
Types of Additive Post-Processing
Advantages & Disadvantages of Additive Post-Processing
Advantages
-
Suitability for End-Use Application
Post-processed parts are more aesthetically pleasing and are ready to withstand the environments in which they will be used.
-
Additive Post-Processing Expertise
You won’t find this level of post-processing craftsmanship anywhere else. We have decades of experience finishing and assembling parts to meet our customers’ strict requirements.
-
Engineering Insights
As part of our DFM process, our experienced engineers can walk you through finishing options to help you select the approach that delivers the best results.
-
Simplify Your Supply Chain
Having us handle these steps in-house saves our customers time and money. Why dedicate precious factory space to finishing your parts when we can do it for you?
-
Speed & Accountability
The same facility that builds your 3D-printed parts also handles the finishing. That means fewer delays (no outsourcing to a third party) and one point of accountability.
-
A Commitment to White Glove Service
Many of our competitors don’t offer post-processing and finishing services. They prefer “print and ship” additive projects. We’re committed to meeting your needs, from design and prototyping to production and post-production.
Disadvantages
-
Adds to Processing Time & Cost
Most additive parts are not ready to use right out of the printer. So when you order them, you need to factor in extra time for post-processing. These extra steps also add to the cost of the parts.
-
You Can’t Skip Post-Processing
Given the current state of additive manufacturing, most parts don’t come off the printer ready to use. They all need some level of post-processing before you can incorporate them into your products.